
What are the warning symptoms of retinal detachment? weak areas in your retina that can be seen by your ophthalmologist (Eye M.D.).previous retinal detachment in your other eye.The following conditions increase the chance of having a retinal detachment:

Fluid may pass through the retinal tear, lifting the retina off the back of the eye, much as wallpaper can peel off a wall. But sometimes the vitreous pulls hard enough to tear the retina in one or more places.

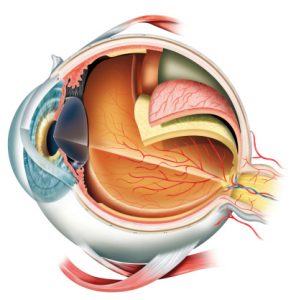
Usually the vitreous separates from the retina without causing problems. As we get older, the vitreous may pull away from its attachment to the retina at the back of the eye. A retinal detachment is a very serious problem that almost always causes blindness unless it is treated.Ī clear gel called vitreous (vit-ree-us) fills the middle of the eye. Vision is blurred, just as a photographic image would be blurry if the film were loose inside the camera. The retina does not work when it is detached. A retinal detachment is a very serious problem that almost always causes blindness unless it is treated.Ī retinal detachment occurs when the retina is pulled away from its normal position. You can think of the retina as the film that lines the back of a camera. The lens in the front of the eye focuses light onto the retina. The retina is a nerve layer at the back of your eye that senses light and sends images to your brain.
Copyright 2006, American Academy of Ophthalmology. Make changes to your yard if necessary so that your pet is unable to exit your property, due to the risk of traffic accidents. Provide your pet with a safe, quiet area to rest, ensuring there are no hazards that may cause accidental injury. If your pet sustains loss of vision, careful management of the environment is necessary, ensure your canine’s environment stays the same, with no changes to furniture layout. If this condition was caused by an underlying chronic illness, discuss whether a therapeutic diet will be beneficial for your pet’s on-going health with your veterinarian. Highly palatable food should be given to encourage nutrition and energy for healing.Īs ocular surgery success is often guarded, particularly due to the high rates of self-trauma, adequate pain relief is vital as well as use of an Elizabethan collar to prevent injury. If your pet requires surgery it is vital to provide him with a warm, dark environment for recovery. Unfortunately, in many cases, the prognosis may be guarded to poor in regards to return of vision, although many pets go on to live high quality lives following blindness. The prognosis for your pet varies on the underlying cause of the retinal detachment. Causes may include cataract formation or complication following ocular surgery, trauma, and glaucoma. Rhegmatogenous detachments these detachments are caused by tears in the retina. Transudative – With the build up of serous subretinal fluid caused by conditions that affect the circulation such as uremia and hypertension. Exudative – With the build up of neoplastic or inflammatory cells caused by metastatic tumors and infections such as brucellosis and cryptococcosis. Hemorrhagic – With the build up of blood caused by conditions such as hypertension, trauma, neoplasia and therapies such as blood transfusions. This highlights the importance of not breeding from animals who suffer from this conditionĪcquired non-rhegmatogenous detachments are caused by an accumulation of fluid or cells between the retina and RPE. There are three main types of retinal detachment in dogs.ĭetachments caused by inherited ocular defects such as collie eye anomaly and retinal dysplasia.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
